To use this operator, you will need to install the de.uniol.inf.is.odysseus.wsenrich.feature.feature.group (found in the incubation update site, https://odysseus.informatik.uni-oldenburg.de/updatesite/odysseus_all_new/incubation/origin/master/latest/)
This operator can be used to access an external web service and enrich incomming elements with the results from the web service. Different processing modes are available, data can be cached.
Parameter:
- serviceMethod: Method by which the web service should be accessed: Possible Values 'REST', 'SOAP' and 'XML-RPC' (beta)
- wsdlLocation: url to the location of the wsdl file, i.e. what is the address of the web service for soap
- operation: operation used to call a SOAP-Webservice/XML-RPC-method
- method: How to access the web service. For REST this is typically GET. Other methods are POST_ARGUMENTS, POST_DOCUMENT
- contentType: The http request header type e.g "application/json".
- url:static part of the url, will be used in request. Remark: For REST and SOAP: Must contain ? to seperate arguments
- templateURl (boolean): If the url is a template, set to true
- template: A template that should be used in a post request as content. Elements are replaced from arguments.
- urlSuffix: url part after argument, will be appended at the end of the url (e.g for further static parts)
- arguments: This is a key value map, first element is the name of the attribute in web service, the second the name of the attribute from the input stream that delivers the input element. For XML-RPC just the order is relevant. You could e.g. use \['1','data'\]
- datafields: the datafields received through the webservice, given as path expressions. Can be attribute names in case of XML-RPC
- charset: the charset, e.g. UTF-8
- parsingMethod: How to extract the values from the returned document: Currently available: 'JSONEXPERIMENTAL','JSONPATH','XMLEXPERIMENTAL','XPATH' (ignored for XML-RPC)
- keyValueOutput: boolean: If true, received Data from a Webservice are returned as keyValuePair (ignored for XML-RPC)
- outerjoin
- multitupleoutput
Caching parameter:
- Caching
- Cachesize
- Expirationtime
- Removalstrategy
Beta-Options (use with care, may not work in any cases!):
- noOfWorkers: Typically, this enrich operator will not use any worker, i.e. the source thread will be blocked, until there is a result. To allow concurrent accesses to the enrichment source, the number of workers can be raised. Because order is still kept, no enriched element will overtake another one.
- keepOrder (Boolean, default: true): When set to false and in combination with noOfWorkers, the output order is no longer guaranteed and the worker that delivers the results first, will send there output directly.
#PARSER PQL
#QUERY
input = ACCESS({
source=’Source’,
wrapper=’GenericPull’,
transport=’File’,
protocol=’CSV’,
datahandler=’Tuple’,
options=[
[’filename’, ’C:\Users\Daniel\Desktop\Test\Testdaten\cityInf.csv’],
[’delay’, ’1’]
],
schema=[[’id’, ’Integer’],[’data’, ’String’]]
}
)
s01 = WSENRICH({
servicemethod=’REST’,
method=’GET’,
url=’http://api.geonames.org/countryInfo?lang=it&’,
urlsuffix=’&username=demo&style=full’,
arguments=[[’country’, ’data’]],
datafields=[
[’//countryCode’, ’String’],
[’//countryName’, ’String’],
[’//isoNumeric’, ’Integer’]
],
parsingMethod=’XPATH’,
outerJoin=’false’,
caching=’true’,
cacheSize=100,
expirationTime=300000,
removalStrategy=’FIFO’
},
input
)
A simple example for an xml-rpc based communication:
Server is from here:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/xmlrpc.server.html
from xmlrpc.server import SimpleXMLRPCServer
from xmlrpc.server import SimpleXMLRPCRequestHandler
# Restrict to a particular path.
class RequestHandler(SimpleXMLRPCRequestHandler):
rpc_paths = ('/RPC2',)
# Create server
with SimpleXMLRPCServer(('localhost', 8000),
requestHandler=RequestHandler) as server:
server.register_introspection_functions()
# Register pow() function; this will use the value of
# pow.__name__ as the name, which is just 'pow'.
server.register_function(pow)
# Register a function under a different name
def adder_function(x, y):
return x + y
server.register_function(adder_function, 'add')
# Register an instance; all the methods of the instance are
# published as XML-RPC methods (in this case, just 'mul').
class MyFuncs:
def mul(self, x, y):
return x * y
server.register_instance(MyFuncs())
# Run the server's main loop
server.serve_forever()
For this, the following (rather silly) odysseus query can be used.
#PARSER PQL
#RUNQUERY
timer = TIMER({
period = 1000,
source = 'timer'
}
)
mapped = MAP({
expressions = [
['1','a'],
['1','b']
],
keepinput = true
},
timer
)
enriched = WSENRICH({
url = 'http://localhost:8000/RPC2',
servicemethod = 'XML-RPC',
datafields = [['result', 'Integer']],
arguments = [['a','a'],['b','b']],
operation = 'add'
},
mapped
)
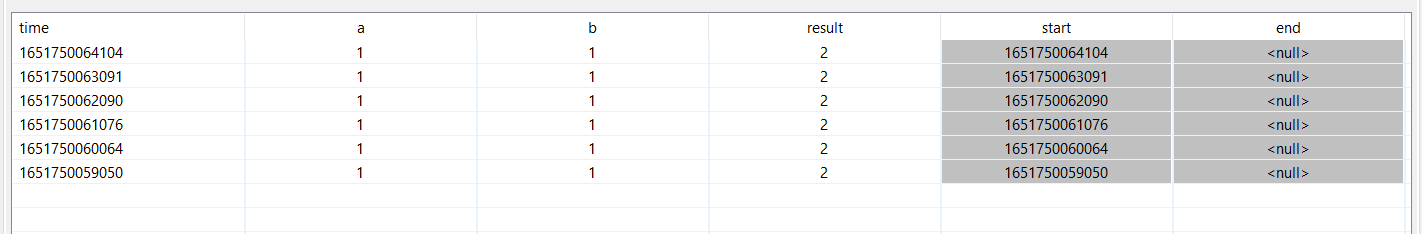
and creates the following output
As you can see. The attribute time is not used for processing, but is still part of the ouput.