In this tutorial you will learn how to combine information from different sources.
We will use the same setting as in Simple Query Processing. So you should follow steps 1-4.
Join
One of the most important operators to combine events from different streams is the join operator.
To combine two elements from different streams, two conditions must hold:
- The time intervals must overlap
- The join predicate must evaluate to true
Create a new PQL based script (join1.qry) with the following input:
| Code Block |
|---|
#PARSER PQL
#TRANSCFG Standard
#ADDQUERY
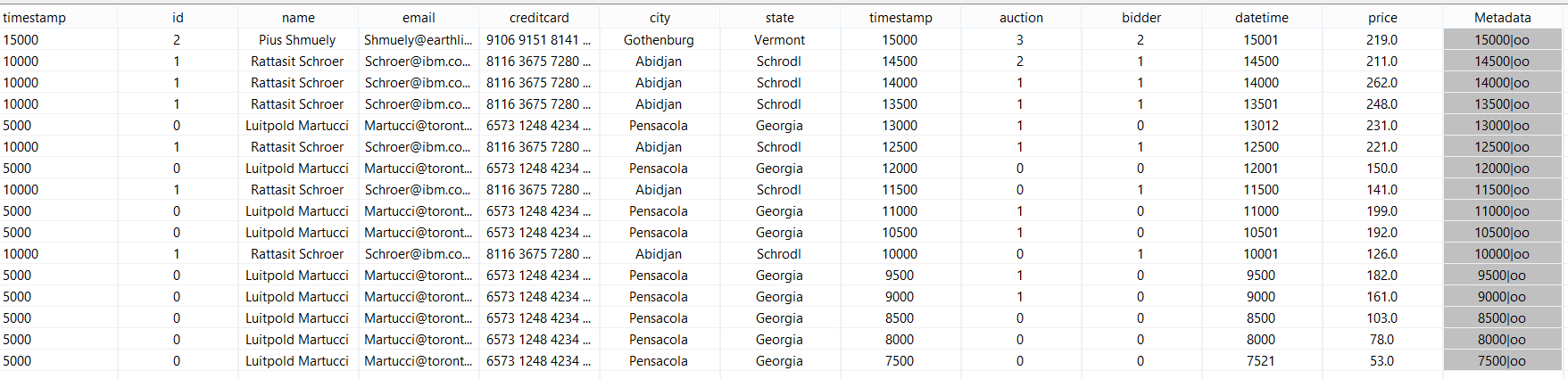
out = JOIN({PREDICATE='nexmark:person.id = nexmark:bid.bidder'},nexmark:person, nexmark:bid) |
This query add to each bid the person that is bidding.
After starting you should see something like in the following.
WARNING: In this example we use no windows. For Joins this is typically not recommended, as it can lead to memory overflow!
In most cases it is easy to define a window for each input stream.
There are some case, where you can speed up processing or cope with the case where no windows can be defined by using the parameter CARD:
- ONE_ONE: In each input stream there is exactly one corresponding object. With this setting, windows can potentially be avoided.
- ONE_MANY: Each element in the right input stream has exactly one corresponding element in the left input stream
- MANY_ONE: Each element in the left input stream has exactly one corresponding element in the right input stream
- MANY_MANY: For each element in both input streams there may be multiple corrsponding elements. This is the default.
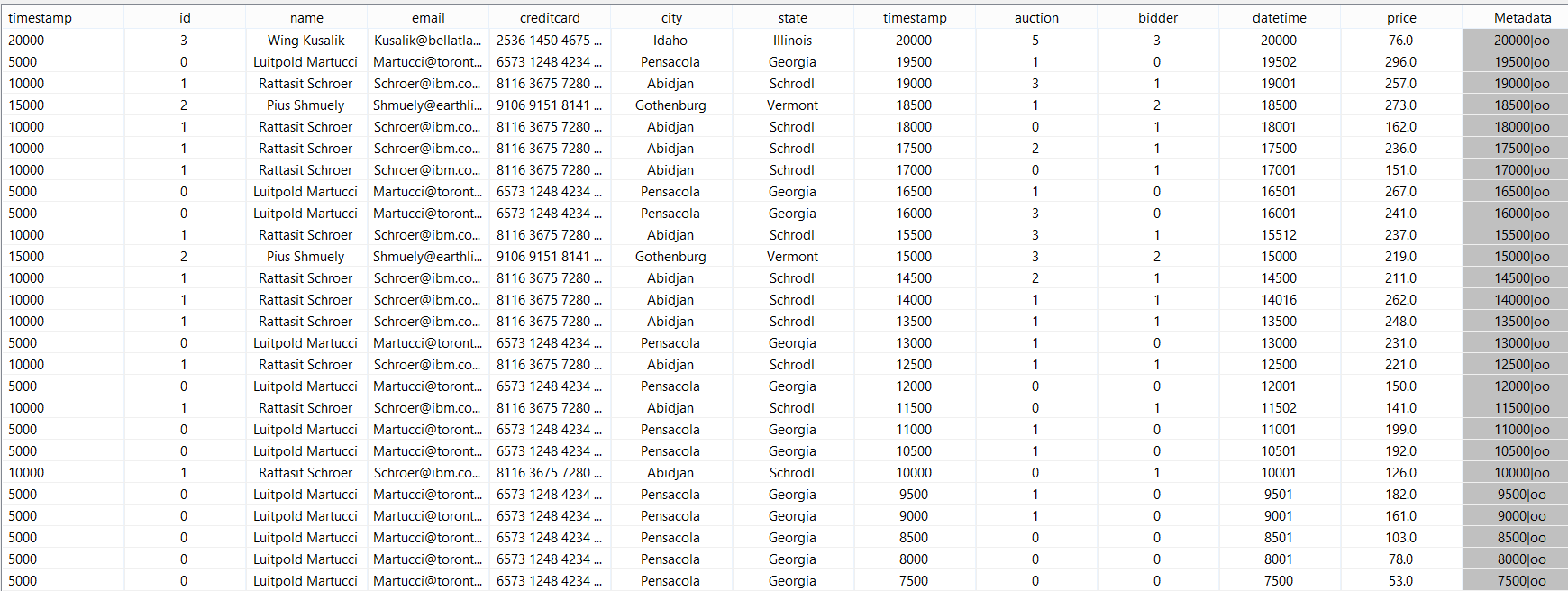
For the example above, each bid has exactly one person. So we can write:
| Code Block |
|---|
#PARSER PQL
#TRANSCFG Standard
#ADDQUERY
out = JOIN({PREDICATE='nexmark:person.id = nexmark:bid.bidder', CARD='ONE_MANY'},nexmark:person, nexmark:bid) |
And this lead to the same output.